Hi mate, good morning! We will be dealing back with our network topology that we configured before.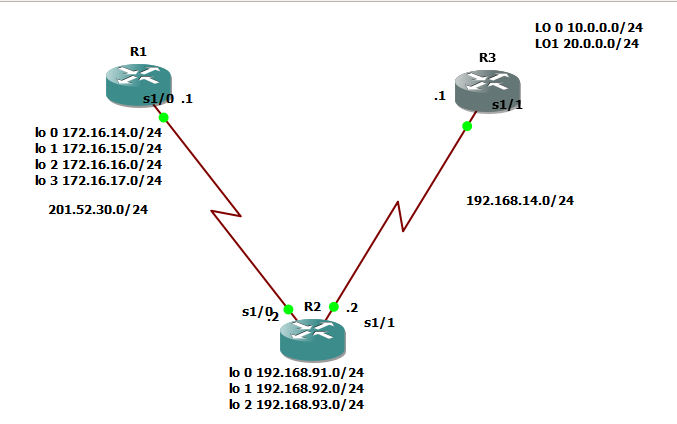
You wonder what is router-id right? Router-id is the identifier of router on the perception of another router. I am sorry if it is a little bit confusing. Here’s how it goes, R1 would identify R2 by R2’s router-id and R2 would identify R1 by R1’s router ID.
I hope that your GNS3 is now ready. Kindly input ” show ip protocols”
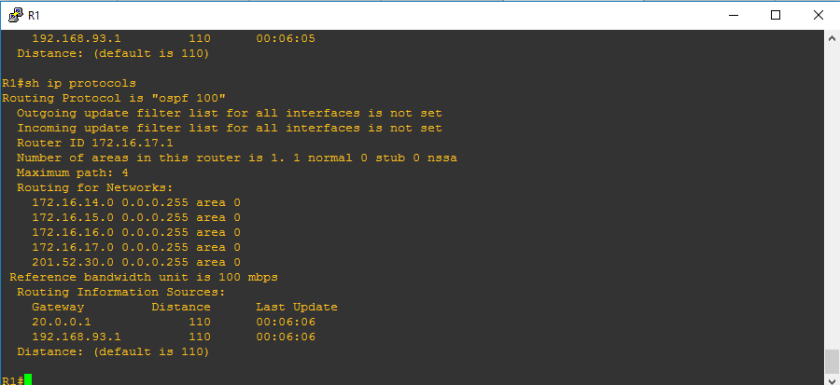
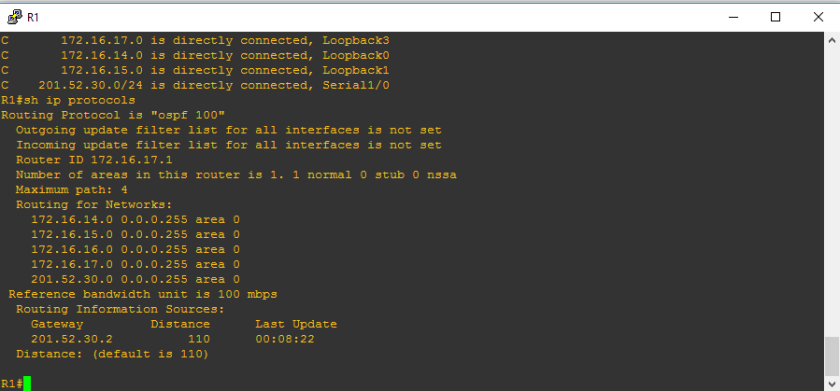
Router-ID is an important concept in each routing protocols specially with OSPF and EIGRP. When R1 would like to connect to R2, of course R1 should introduce himself and R1 will introduce his router-id as his name. On the figure above, you would see ROUTING INFORMATION SOURCES and the ip address written on the gateway column is the router-id. So how would we know the router-id which should be listed? There are hierarchy to know the router-id and these are the following from the top priority to the least priority.
1.) Hard-coded router-id – this is the router-id that we manually configure.
2.) Highest loopback address- very self-explanatory, the loopback address which has highest numerical value
3.)Highest ip address- very self-explanatory, the ip address which has highest numerical value
If ever you wonder why there are two router-ids on the “show ip protocols” command, it was because there are two neighbor routers.
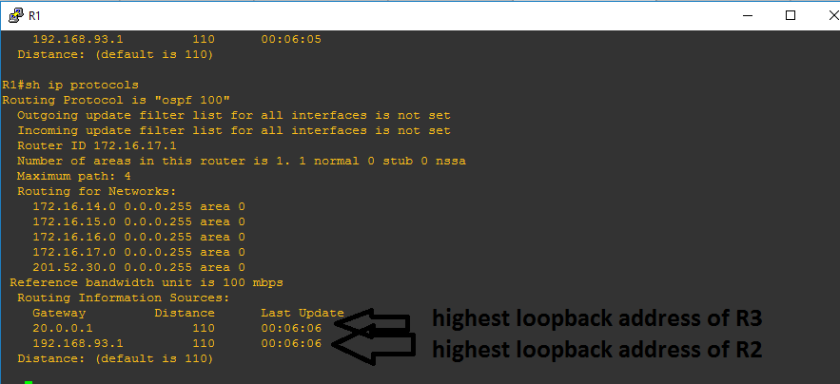
Before we proceed with manually configuring the IP address, let us try to remove the loopback addresses, to know if removing the loopback address would lead us that the highest IP address will be the last resort if there are no loopback address and no hard-coded router-id. Since it is very obvious on the figure above that highest loopback address was used instead of hard coded router-id and highest IP address.
Let us try to implement:
on R2
conf t
int lo 0
ip address 192.168.91.1 255.255.255.0
shut
int lo 1
ip address 192.168.92.1 255.255.255.0
shut
int lo 2
ip address 192.168.93.1 255.255.255.0
shut
exit
do sh ip int br
on R3
en
conf t
int lo 0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
shut
int lo 1
ip address 20.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
shut
exit
do sh ip int br
As you observed, the router-ids are not changed. Why is it happening? because R1 already knows R2 as 192.168.93.1 and R1 already knows R3 as 20.0.0.1 and so in the event there are changes with R2 and R3, R1 would still identify R2 and R3 as their original router-ids unless R2 and R3 reintroduce themselves to R1. In order that R2 and R3 will reintroduce themselves to R1, we need to restart the routers.
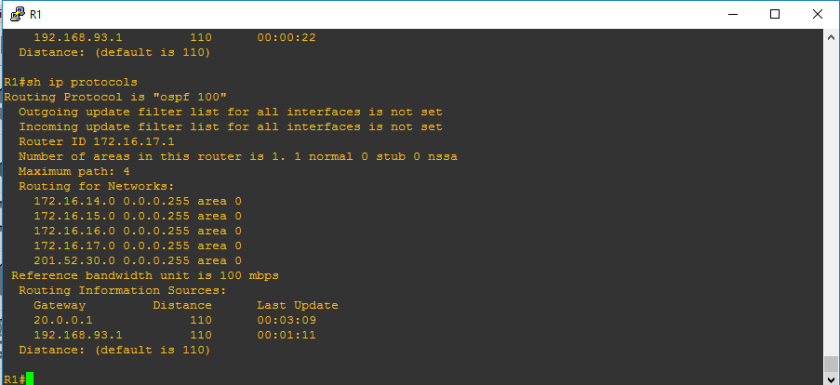
Alright, the routers just got restarted, and let us check sh ip protocols command,
You would see that 201.52.30.2 which is not a loopback nor hard-coded router-id on the routing information sources. Due to incorrect configuration, only one router-is is known by R1 and R3’s router-id is not known by R1. Also, you will see above the the router-id of R1 still remain as 172.16.17.1 since we did not touch that.So let us retrieve the loopback addresses.
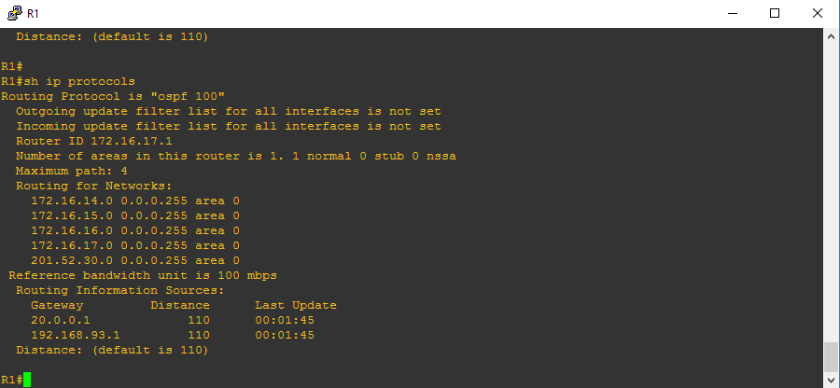
***********************************************************************Configuration of Router-IDs
Mate, it is very clear that the reason why we consider hard-coded router-ids as top of the hierarchy is because it is something stable or meaning to say it will not vary. What I mean is that in the event that the interface with highest ip address went down or the loopback address was accidentally went to administratively down, it may cause misconfiguration which will lead to network disruption.So it is advisable in the industry, to configure router-id. So let us take note that router-id doesnt necessarily mean that it is an ip address though it looks like ip address.
Let us designate the router-ids of routers:
R1 1.1.1.1
R2 2.2.2.2
R3 3.3.3.3
SYNTAX:
en
conf t
router ospf {process#}
router-id x.x.x.x
do clear ip ospf process —> it will appear and it is your discretion whether to restart router or clear the router-ids, then type YES
do wr
exit
do sh ip protocols
@R1
en
conf t
router ospf 100
router-id 1.1.1.1
do clear ip ospf process ; type YES
do wr
exit
do sh ip protocols
@r2
en
conf t
router ospf 100
router-id 2.2.2.2
do clear ip ospf process; type YES
do wr
exit
@R3
en
conf t
router ospf 100
router-id 3.3.3.3
do clear ip ospf process; type YES
do wr
exit
And there you go, we will check the router-id of R1, please take note that old router-ids may take time to be removed on the sh ip protocols table
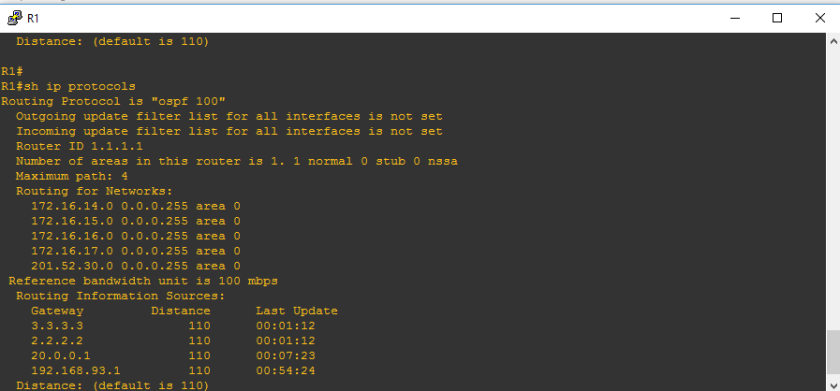
Let’s check R2
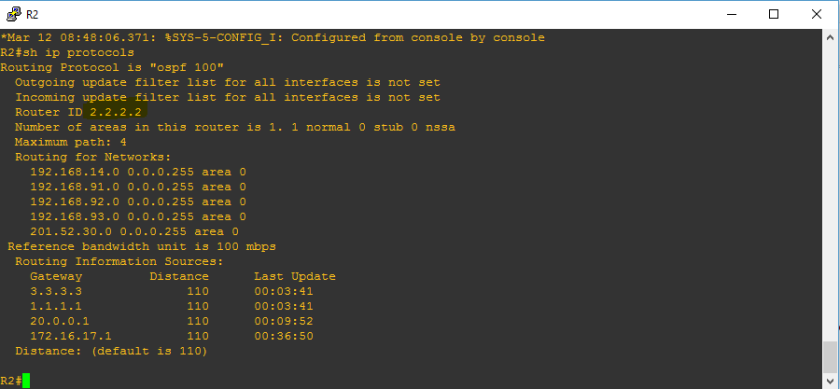
Let’s check R3
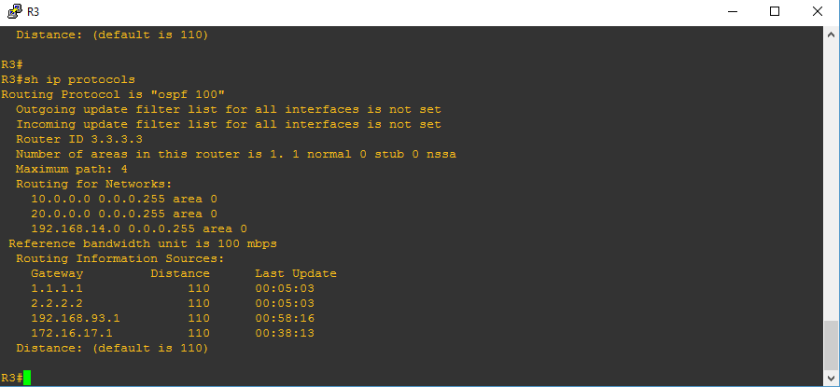
And there dyou go! We are able to at least configure router id on OSPF protocol. Next ospf process that we will configure is passive inteface and security features of OSPF. After that, we will explain how OSPF works. Stay tuned!
